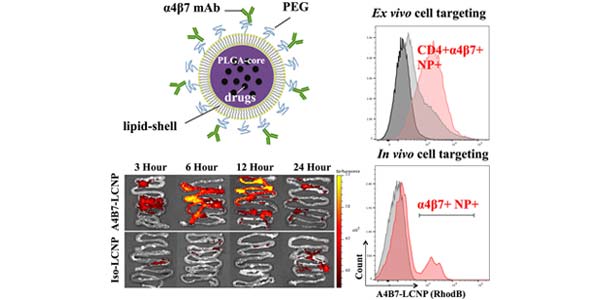
Image: We developed core-shell nanoparticles incorporating the a4B7 monoclonal antibody (mAb) for selectively delivering therapeutic agents to gut-homing T cells in the gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT), while simultaneously blocking HIV infection. We demonstrate enhanced antiretroviral activity of a protease inhibitor and a4B7 mAb combination in vitro, and show targeting function in rhesus macaque primary cells and in mice. These data demonstrate that our LCNP delivery system has the potential to co-deliver ARV drugs and mAbs to anatomical and cellular HIV reservoirs for the purpose of reducing reservoir size and potentially eradicating the virus.
Core-shell nanoparticles for targeted and combination antiretroviral activity in gut-homing T cells
Shijie Cao, B.S.; Yonghou Jiang, Ph.D.; Hangyu Zhang, Ph.D.; Nina Kondza, B.S.; Kim A. Woodrow, Ph.D.
Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology and Medicine. Volume 14, Issue 7, October 2018, Pages 2143-2153.
Abstract
A major sanctuary site for HIV infection is the gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT). The a4B7 integrin gut homing receptor is a promising therapeutic target for the virus reservoir because it leads to migration of infected cells to the GALT and facilitates HIV infection. Here, we developed a core-shellnanoparticle incorporating the a4B7 monoclonal antibody (mAb) as a dual-functional ligand for selectively targeting a protease inhibitor (PI) to gut-homing T cells in the GALT while simultaneously blocking HIV infection. Our nanoparticles significantly reduced cytotoxicity of the PI and enhanced its in vitro antiviral activity in combination with a4B7 mAb. We demonstrate targeting function of our nanocarriers in a human T cell line and primary cells isolated from macaque ileum, and observed higher in vivo biodistribution to the murinesmall intestines where they accumulate in a4B7+ cells. Our LCNP shows the potential to co-deliver ARVs and mAbs for eradicating HIV reservoirs.