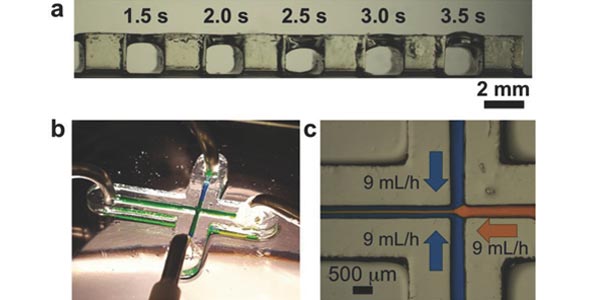
Desktop-Stereolithography 3D-Printing of a Poly(dimethylsiloxane)-Based Material with Sylgard-184 Properties
Professor Albert Folch's lab reports on the formulation, characterization, and SL application of a 3D?printable PDMS resin (3DP?PDMS) based on commercially available PDMS?methacrylate macromers, a high?efficiency photoinitiator and a high?absorbance photosensitizer. 3DP?PDMS resin enables assembly?free, automated, digital manufacturing of PDMS, which should facilitate the prototyping of devices for microfluidics, organ?on?chip platforms, soft robotics, flexible electronics, and sensors, among others.
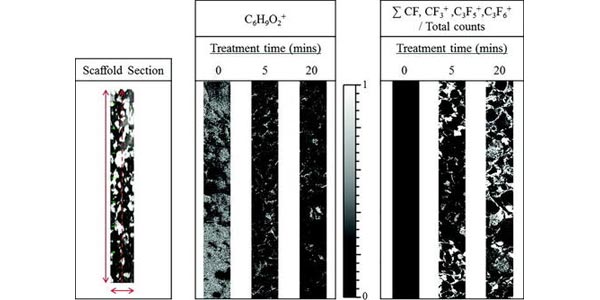
Time of flight secondary ion mass spectrometry—A method to evaluate plasma-modified three-dimensional scaffold chemistry
Research Associate Professor Lara Gamble and colleagues report on a technique for characterizing the distribution and composition of chemical species through complex porous scaffolds. This approach could be widely applicable for ToF-SIMS analysis of scaffolds modified by multiple plasma processing techniques as well as alternative surface modification approaches.
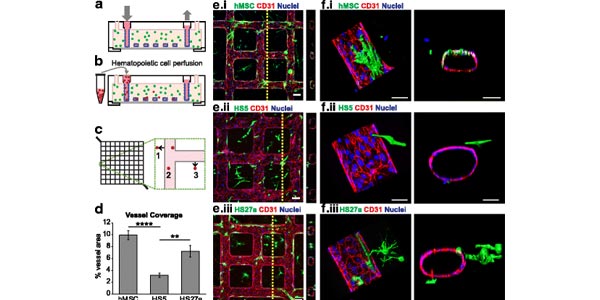
Engineering a multicellular vascular niche to model hematopoietic cell trafficking
Assistant Professor Ying Zheng and colleagues developed an engineered human vascular marrow niche to examine the three-dimensional cell interactions that direct hematopoietic cell trafficking. The platform provides a tool to advance study of the interactions between endothelial cells, marrow-derived fibroblasts and hematopoeitic cells that comprise the marrow vascular niche, and has potential for use in testing therapeutics and personalized medicine.
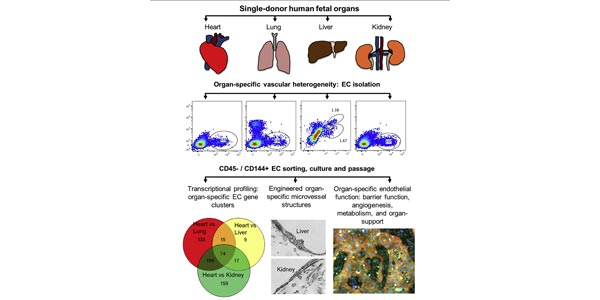
Human Organ-Specific Endothelial Cell Heterogeneity
BioE faculty Charles Murry, Kelly Stevens and Ying Zheng, and interdisciplinary colleagues from across UW, investigated the properties of endothelial cells (ECs), isolated from four human major organs—the heart, lung, liver, and kidneys—in individual fetal tissues at three months' gestation, at gene expression, and at cellular function levels. Their findings showed the link between human EC heterogeneity and organ development and can be exploited therapeutically to contribute in organ regeneration, disease modeling, as well as guiding differentiation of tissue-specific ECs from human pluripotent stem cells.
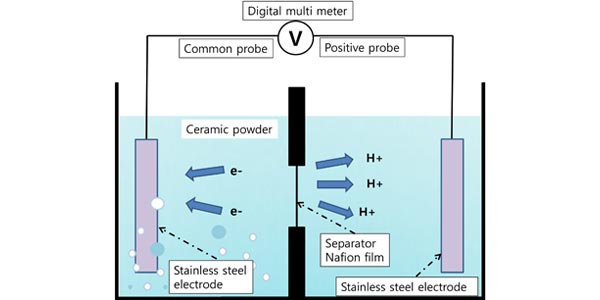
Exclusion zone and heterogeneous water structure at ambient temperature
Professor Gerald Pollack and colleagues report the formation of a ‘three-dimensional cell-like structured exclusion zone’ in water prepared by two different methods. Based on their findings of an electric potential difference between the heterogeneous structured water and the ordinary water, the researchers propose a new model to explain the relationship between heterogeneous, structured water and its electrical properties.
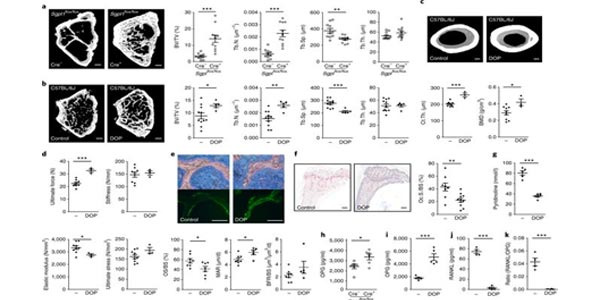
Targeting sphingosine-1-phosphate lyase as an anabolic therapy for bone loss
Research Associate Professor Marta Scatena and a team of collaborators show that raising Sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) levels in adult mice through conditionally deleting or pharmacologically inhibiting S1P lyase, the sole enzyme responsible for irreversibly degrading S1P, markedly increased bone formation, mass and strength and substantially decreased white adipose tissue.